
20 Nov, 2025
Feel free to reach out to us.

20 Nov, 2025

This article is medically reviewed by Dr. Sachin Trivedi, Consultant - Medical Oncology, HCG ICS Khubchandani Cancer Centre, Colaba, Mumbai
Chemotherapy is one of the most common treatments for cancer. It involves administering cytotoxic drugs to treat various types of cancer. The cytotoxic drugs either kill the cancer cells or inhibit their growth, division, and proliferation.
Oncologists may prescribe chemotherapy as a curative, adjunctive, or palliative therapy. Several routes for administering chemotherapy drugs exist, including oral, intravenous, and intramuscular. The dose of the chemotherapy drugs is determined according to the stage of the disease, extent of spread, drug resistance, and toxicity data of the drug.
Chemotherapy may be administered as a primary treatment or combined with surgery or radiation therapy. It is administered before the surgery (neoadjuvant therapy) to shrink the tumor size or after the surgery (adjuvant therapy) to kill the remaining cancer cells, and it is one of the most effective ways to reduce cancer risk the second time. Adjuvant therapy is usually prescribed for lung, breast, ovarian, and colorectal cancers.
Radiation therapy is an important tool for the management of various types of cancer. It involves delivering ionizing radiation to the tumors, which damages their DNA and interferes with other vital processes. It also causes the death of tumor cells and the shrinkage of tumors.
At least 50% of patients with cancer undergo radiation therapy during their disease management course. The total radiation dose planned is delivered in multiple sessions to optimize cancer cell damage and minimize side effects.
Chemotherapy and radiation therapy are the primary treatments for the management of several types of cancer. They are generally used in combination.
The choice of either chemotherapy or radiation therapy depends upon several factors, such as the type of cancer, the stage of the disease, its grade, the exact location of the tumor, and the patient’s age and overall health.
Both chemotherapy and radiotherapy are very effective cancer treatments that are administered while managing
different types of cancer. They may be used in combination with each other or in combination with other
treatments, such as surgery, for enhanced treatment efficacy.
Chemotherapy works by targeting cancer cells throughout the body, whereas radiotherapy works by targeting
cancer cells in a particular area with powerful radiation beams.
The following are the differences between chemotherapy and radiation therapy:
Chemotherapy and radiation therapy have different underlying mechanisms. However, both treatment modalities have a common goal: to kill cancer cells and control their growth.
"Chemotherapy, a prevalent cancer treatment, involves cytotoxic drugs that target cancer cells, which is
administered via oral or intravenous, and the dosages are tailored to disease stage and patient
response. It can be curative, adjunctive, or palliative, often used alongside surgery or radiation.
"
Dr. Sachin Trivedi
Cytotoxic drugs use several mechanisms to kill cancer cells. The mechanisms depend on the types of chemotherapy drugs. These drugs are classified based on their mechanism of action.
Alkylating agents inhibit DNA replication and transcription. Anti-metabolites inhibit DNA replication. Anti-microtubular agents and certain antibiotics interfere with the synthesis of RNA and DNA.
"Radiation therapy plays a crucial role in treating cancer by targeting tumors with ionizing radiation.
This damages cancer cells' DNA, leading to cell death and tumor shrinkage. Various types of ionizing
radiation are used, customized to minimize harm to healthy tissues."
Dr. Sachin Trivedi
The procedure of radiation therapy involves the use of ionizing radiation to damage cancer cells. The most common types of ionizing radiation used to manage cancer include photons and electrons.
Other ionizing radiations include carbon ions, protons, and neutrons. The dose for each radiation is optimized to minimize damage to healthy tissues.
When radiation beams fall on cancer cells, they break the double-stranded DNA, resulting in a phenomenon known as mitotic catastrophe. Rapidly dividing cells, such as those of the gastrointestinal system and oral mucosa, are more sensitive to radiation therapy.
Several routes are available to deliver the chemotherapy drugs. The choice of route depends on the type of cancer.
The different routes available for the administration of chemotherapy drugs include oral administration; intra-arterial route for liver, brain, and head and neck cancers; intrathecal route for leukemia, lymphoma, and breast cancer; intrapleural route for lung cancer; intraperitoneal route for colorectal cancer; isolated limb perfusion in melanoma; and intra-tumor route for superficial bladder cancer and cancerous lymph nodes.
Delivery of radiation therapy for cancer is done through two methods.
External beam radiation therapy, known as teletherapy, is one of the most frequently used methods for radiation therapy. This process involves delivering ionizing radiation to the tumor cells through a radiation source (a linear accelerator) outside the body.
Radiation oncologists use various techniques, namely intensity-modulated radiation therapy, image-guided radiation therapy, stereotactic radiation therapy, stereotactic radiosurgery, total body irradiation, and more.
These advanced techniques help in precisely targeting the tumor for radiation delivery and minimizing damage to nearby healthy tissues.
The other method for delivering radiation therapy is brachytherapy. Also known as internal beam radiation therapy, it involves placing radioactive material beside the tumor or directly inside it.
The advantage of brachytherapy over external beam radiotherapy is that it allows physicians to deliver a higher radiation dose in a smaller area within a shorter time. It also helps reduce damage to healthy tissues close to the tumor.
Patients undergoing chemotherapy experience various side effects. These side effects are explained by the mechanism of action of these drugs, which involves the targeting of rapidly dividing cells, which include both cancer cells and healthy cells, such as bone marrow cells, hair follicles, and cells of the gastrointestinal tract.
Some of the common side effects of chemotherapy are mucositis, hair loss, fatigue, vomiting, diarrhea, infertility, nausea, and immunosuppression. Patients are at high risk for infection because of immunosuppression.
The after-effects of radiation therapy are usually divided into acute, late consequential, and later side effects. The acute side effects are due to damage to the rapidly dividing cells, such as skin cells and the cells that line the digestive tract.
When the acute side effects do not heal completely, they progress to the late consequential stage. These complications occur commonly in people undergoing a combination of chemotherapy and radiation therapy when the effects of cancer drugs do not allow the tissue to heal completely.
Patients may also experience late complications months or years after radiation exposure. The organs commonly affected by late complications are the kidney, brain, liver, muscles, intestine, and fatty tissues.
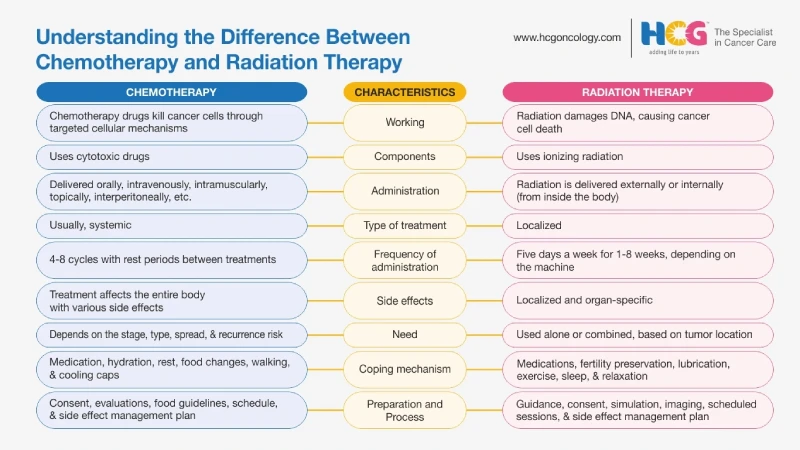
The biggest difference between chemotherapy and radiation therapy is the approach with which they target the cancer cells.
Chemotherapy is a systemic approach wherein powerful anti-cancer drugs are used to kill cancer cells throughout the body. Radiotherapy, on the other hand, is a localized treatment approach, and only cancer cells in a specific region are targeted with radiation beams.
The following table elucidates the key differences between these two powerful cancer treatment approaches:
| Characteristics | Chemotherapy | Radiation Therapy |
|---|---|---|
| Components | Uses cytotoxic drugs | Uses ionizing radiations |
| Administration | Oral and injectable | External beam radiation and brachytherapy |
| Type of treatmen | Usually, systemic | Localized |
| Frequency of administration | Multiple cycles over several weeks with a resting period in between | Given almost daily over 1-9 weeks, depending on individual case parameters and the linac used for the treatment. |
| Side effects | Widespread side effects due to its ability to travel throughout the body and attack cancer cells systemically. | Side effects are usually localized and specific to the organ that is treated with radiation. |
Depending on the individual case parameters and treatment goal, specialists may recommend chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or both. These treatments can be recommended for remission, disease control, and symptom management.
The choice of chemotherapy as a treatment modality for managing cancer depends on several factors, such as stage of disease diagnosis, disease progression, types of cancer, and its location. The doctor may use chemotherapy as a primary mode of treatment.
Chemotherapy may also be prescribed before or after the surgery when the treating oncologist believes that the patient is at increased risk of the cancer spreading to other parts or is at elevated risk for recurrence.
Radiation therapy may be used as a primary treatment, sometimes the only treatment needed, or it may be used along with other treatment modalities, such as surgery or chemotherapy, in patients with advanced cancer.
The choice of radiation therapy as a treatment for cancer depends on various factors, such as the location of the tumor, the overall health of the patients, and their age.
Radiation therapy is administered to shrink or cure early-stage cancer, stop cancer recurrence, treat recurrent cancer, and manage symptoms caused by advanced cancer.
Several patients wonder and worry about what happens in chemotherapy. However, it is a safe treatment approach, and only after a detailed discussion with the patient will the care team proceed further with the treatment.
Watch this video, where our specialists from HCG Mumbai discuss the myths that surround chemotherapy:
Medical oncologists and other members of the care team carefully study the individual case parameters before recommending chemotherapy as a treatment option.
Before chemotherapy, the patients meet the oncologists, receive detailed information about the chemotherapy treatment schedule, and offer their consent for chemotherapy. It is also important to ask the doctor about the effect of food and other medications on chemotherapy.
Planning for the chemotherapy process is an important step. The possible side effects of the treatment and measures to manage them may be discussed before the treatment begins.
Patients may expect comprehensive body evaluation before chemotherapy. It may include blood testing and measuring blood pressure, breathing rate, pulse, oxygen saturation, and temperature.
To optimize treatment outcomes, patients should adhere to the guidelines shared by medical oncologists before and after chemotherapy.
Anxiety in patients is common when radiation therapy is recommended to them. However, providing them with the appropriate information and guidance about radiation therapy helps make them comfortable.
The radiation therapy team comprises radiation oncologists, radiation oncology nurses, dosimetrists, and medical radiation physicists. Patients will be given instructions to be followed before and after radiation therapy, and they need to adhere to them.
Hospital management may ask the patients to fill out the informed consent form. The patients may also undergo simulation and treatment planning that involves practicing the treatment without radiation.
The patients may also be asked to undergo imaging scans to confirm the tumor location right before the treatment.
One session of external beam radiation therapy lasts for about 15 minutes. Patients may generally require 4 to 5 times per week for 3 to 9 weeks, depending on the type and severity of the disease.
Patients undergoing brachytherapy may expect permanent or temporary placement of the radioactive sources at the tumor site.
Watch this video, where specialists from HCG Ahmedabad are answering burning questions about radiotherapy:
Patients undergoing chemotherapy may experience various side effects. However, because of the advancements in medicine, it is possible to manage these side effects successfully.
Side effects, such as nausea and vomiting, can be effectively managed through medication. Patients should hydrate themselves by drinking fluid. Modifying food habits may help address the taste change caused by chemotherapy.
Doctors may also advise the patients to take appropriate rest and focus their energy on important things. Patients may also take a short walk to improve their stamina.
Patients may also use cooling caps during chemotherapy to reduce hair loss. Ice chips during treatment may also help reduce the oral side effects of chemotherapy.
Various options are available for managing the side effects of radiation therapy. Doctors may prescribe medications for depression, erectile dysfunction, dermatitis, mucositis, nausea, and vomiting.
Egg and sperm preservation is also an option to manage infertility. Vaginal dryness can be managed through lubrication. Fatigue can be managed through exercise, following appropriate sleep hygiene, stress reduction, and other cognitive and relaxation therapies.
Both chemotherapy and radiotherapy treatments are recommended after the careful evaluation of the patient’s condition, disease stage and grade, and the patient’s overall condition. The duration of both chemotherapy and radiation therapy varies depending on various factors. Both radiotherapy and chemotherapy cause various side effects, which are manageable and wear off in some time after the treatment.
HCG ICS Khubchandani Cancer Centre, Colaba, is the best cancer hospital in Mumbai with the availability of advanced treatment options for patients dealing with a broad spectrum of cancers.
The treatment facilities provided by this hospital include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, surgery, and other modern systemic therapies, namely targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and hormone therapy.
The hospital is equipped to deliver chemotherapy drugs through all administration routes and has a daycare chemotherapy center to support outpatient chemotherapy. The chemotherapy team also provides care to the patients in managing side effects.
HCG ICS Khubchandani Cancer Hospital also offers external beam radiation therapy and brachytherapy to patients. The center also provides CyberKnife treatment to precisely target the tumor and reduce the dose of radiation.
If you are looking for the best radiation oncologist in Mumbai or the best medical oncologist in Mumbai, your search ends here.
Chemotherapy and radiation therapy are pivotal in cancer management, each with distinct mechanisms and effects.
Chemotherapy employs cytotoxic drugs to inhibit cancer cell growth, while radiation therapy utilizes ionizing radiation to damage cancerous DNA. There are certain radiation and chemo differences, and understanding these differences is crucial for patients to know what to expect during their treatment.
Treatment selection hinges on factors like cancer type, stage, grade, location, the patient’s age, and overall health.
Both therapies entail side effects, yet chemotherapy's impact is systemic, whereas radiation therapy's effects are localized. Patient expectations and coping strategies vary but aim to mitigate adverse effects for better treatment outcomes.

Dr. Sachin Trivedi
MBBS, MRCP (London), MRCP (Medical Oncology), SCE (Medical Oncology), CCST,
FRCP (Edin), PhD
Consultant – Medical Oncology
Dr. Sachin Trivedi is a highly accomplished medical oncologist practicing at HCG ICS Khubchandani Cancer Centre, a leading cancer hospital in Mumbai. with expertise in managing a wide range of cancers using systemic therapies. Specializing in head and neck cancers, breast cancer, lung cancer, and GI cancers, he excels in all forms of systemic therapies and precision medicine. He focuses on treating his patients with a personalized and holistic approach. Dr. Trivedi's extensive experience also includes cancer genomics, preventive oncology, and clinical trials.
If you are looking for the best medical oncologist in Mumbai, the solution lies before you. To book an appointment with Dr. Sachin Trivedi, please click here.